Description
Intended for use as a domestic textile, a cover.
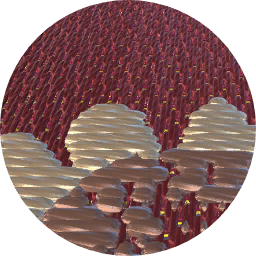
Phulkari ('flower work') was produced in northern India, particularly in the Punjab, where Caspar Purdon Clarke acquired his examples. Designs are embroidered onto evenly woven cotton cloth (khadi, khaddar) usually dyed terracotta red or indigo blue. Narrow strips of cloth are often joined together to make the whole piece. Untwisted soft floss silk (heer, pat) is used, mostly yellow and white, which reflects the light, lending a lustrous appearance to the finished piece. There are different types of phulkari work. Some leave parts of the cloth empty as part of the design. Hindu pieces usually include images of figures and animals; Muslim and Sikh work have geometric designs. In the type known as bagh ('garden', 'ground'), almost the whole surface of the cloth is covered with patterns done in surface darning stitch. Double running stitch was used for other designs, and a variety of additional stitch types added. Phulkari was made for everyday clothes and especially for ceremonial wear at weddings and festivals. Each type has a special name, such as Bagh, Chope, Sainchi, Darshan Dar, Vari da Bagh. Shishadar or sheesh bagh incorporates mirror work.
Phulkari textile, head cover, coarse cotton dyed terracotta red, embroidered with floss silks in gold and yellow with pink, green and white. Made of strips of cloth joined. The field is embroidered with a lattice design containing a geometric motif, the ends have a flower and leaf design. Complete piece.
Textile, cover, phulkari, cotton embroidered with floss silk, Delhi, ca. 1855-1867